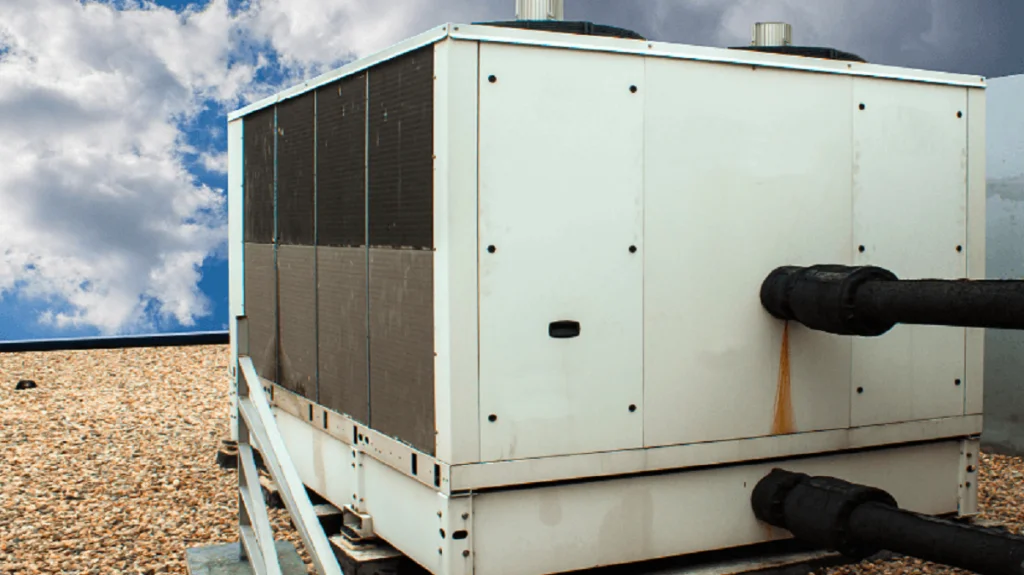
Melting down the efficiency barrier with a water chiller system…Buy an industrial chilled water cooling system to chill your internal machines’ components and processes when your facility uses heavy machinery and fluids that generate heat. These systems don’t have to work harder if the outdoor conditions worsen.
With its versatile and easy application, these industrial chill water systems are widely used in food, electroplating, business card printing, machinery, and other industries. However, these water chillers control plastic temperature and speed up the setting process. Get an overload protector, pressure switches, and electronic alarm functions; VEVOR chill water systems are durable and provide long-term services.
Understand how water chillers work to make the right choice for your cooling needs.
Table of contents
Understanding Chilled Water Systems
In a chiller, heat is removed from the chilled water loop and a compressor from compressing it. These chill water systems are beneficial where temperature requirements are strict. An integrated chilled water cooling system with a heat-sensitive process prevents thermal damage to process equipment and avoids excessive temperature affecting the product.
Water chillers are derived by two operations: vapor compression and heat absorption.
Heat Absorption Chillers: These chillers are constructed to eliminate heat from the associated process through heat exchangers. Most heat exchangers are built-in pipes that coolant fluids.
Vapor Compression Chillers: These chillers cool the process by circulating coolant through the cooling process. Then, a refrigerant system cools the chiller fluid and prepares it for the new cooling cycle.
A water chiller system consists of four essential components: a condenser, a compressor, an evaporator, and an expansion unit. In every water chiller system, refrigerant is built. An evaporator is first used to pass through a low-pressure refrigerant. When heated, a refrigerant undergoes a phase change. After this, the gaseous refrigerant goes into a compressor, which increases its pressure.
Chilled Water System Diagram: A Visual Guide
The water chiller system is made up of two main loops and circuits. The water chiller system produces the cooling through a refrigeration loop. Then, the chilled water loop is a distribution system supplying cold water to consumer units. So, the heat transfer is the main process involved in this system.
The Compression Cycle
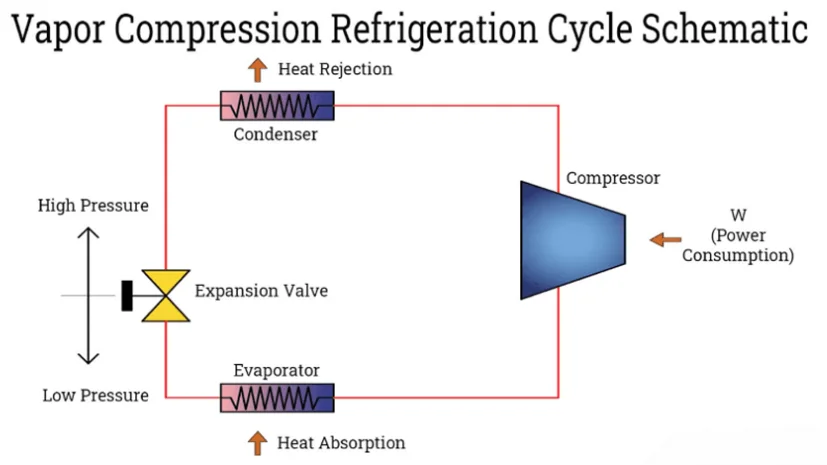
A refrigeration loop works under the principle of a vapor compression cycle. This is a phase of the chemicals during this cycle; a refrigerant changes from liquid to gas and gas to liquid using heat exchangers. For pressuring and depressuring, expansion and compressors are used. Get a brief view of the vapor compression cycle below.
Compression
The refrigerant, as is the ambient air, is at a low pressure at the beginning of this cycle. From the evaporator, it carries the heat absorption.
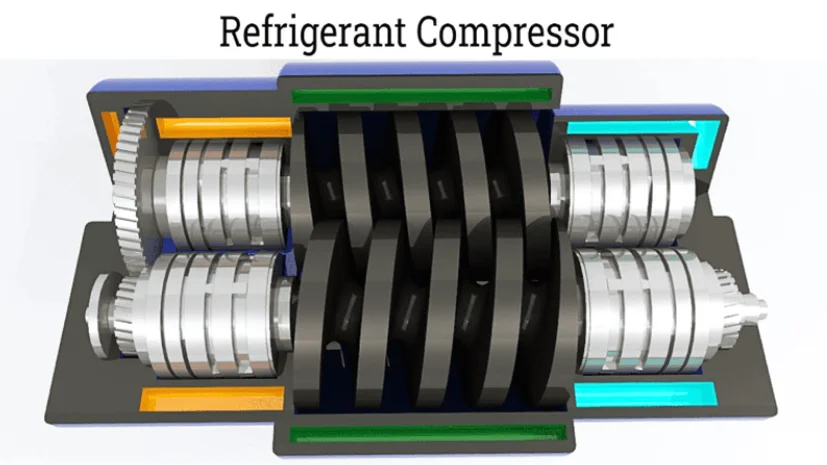
The vaporized detergent is pressurized by the compressor and discharged to a high-pressure side. The temperature of the refrigerant becomes higher at that point. Additionally, mechanical energy gets expanded to increase the pressure of the refrigerant. The compressor operates shaft power to increase refrigerant pressure. During this process, the power is inputted into the system.
Condenser
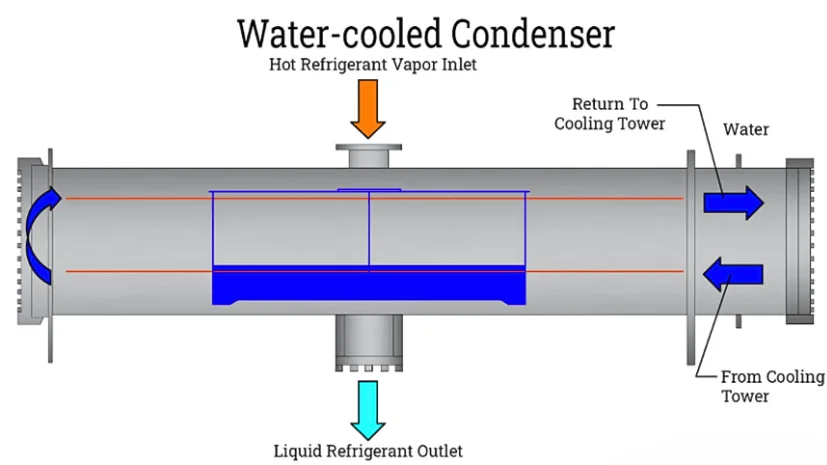
Through this condenser unit, heat gets eliminated from the refrigerant. Depending on the chiller type, water is pumped between the condenser and the cooling tower, and air is blown through condenser pipes.
Expansion
At first, the liquified refrigerant is in a high-pressure state at ambient temperature. Refrigerant pressure decreases during the expansion process. With the depressurizing of the refrigerant, the corresponding temperature also becomes lower.

A small amount of refrigerant lowers its temperature when it flashes and turns into vapors. This process occurs without energy or heat transfer. There’ll be a low-pressure flow after expansion. The expansion process takes place using an expansion device. The capillary tubes and thermal expansion valves are the typical expansion devices.
Evaporator
Evaporator- a low-pressure side of the chilled water system where refrigerant and cooling systems exchange occur. Water and brines are the cooling medium for water chillers.

The refrigerant absorbs heat from the water in an evaporation process. Until the vaporization, it elevates the refrigerant temperature. Water chillers with vapor compression are used in more than 90% of HVAC systems. The absorption refrigerant cycle is the least popular refrigerant cycle. Through an absorption refrigerant cycle, water chillers are cooled, which are called absorption chillers.
Absorption Chillers
In industrial areas, absorption chillers are used where a large steam supply or heat is available. Instead of a compressor, a heat exchanger and other components are used in absorption cooling.
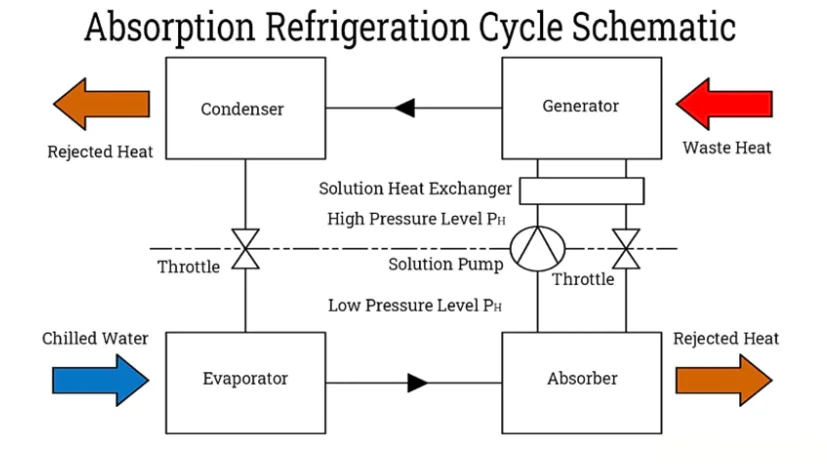
However, at this stage, the compressor doesn’t eliminate much power.
Choosing the Right Water Chiller for Your Needs
Buying a chill water system for specific needs requires planning. You must look at the factors before buying a chiller, for example, size, voltage, temperature, etc. Before investing, keep in mind these details that match your specifications. Here are some aspects that may help you influence your decision:
Size
An oversized water chiller system can consume unnecessary energy. So efficiency and size go hand in hand. However, undersized chillers make you suffer for your facility’s needs. So, to determine the correct chiller size, you must figure out your equipment temperature and heat load—flow rate, etc.
Safety
For your equipment, it’s crucial to install a safe chiller. An explosion-proof chiller is necessary to work in hazardous conditions and process flammable chemical work. So, always buy the designed system that meets the safety standards.
Voltage
Some chilled water systems require specific electrical work. Determine what type of voltage your facility needs and how much electrical budget your work is allowed. Talk to your manufacturer about the best voltage options your system can support.
Temperature
For precise temperature control, a high-quality chiller is required. The custom-designed water chiller system prevents damage and operates your system efficiently. For a temperature below 35C, you may require a low-temperature chiller. Selecting the right chiller ensures your business activities continue without failure.
With the VEVOR portable water chiller, a 15HP Panasonic compressor ensures the chiller runs stably and reliably. Experience a high work efficiency with less vibration and noise and elevate your business to the next level. This water chiller system is a built-in 150L stainless steel water tank for a facilitated operation. However, the water flow is 3.5, whereas the pipe diameter is DN1 in/DN25 mm.
Common Applications of Water Chillers
There are endless industrial applications requiring primary and secondary chilled water systems. Below are the following areas where water chiller systems are used:
- Meta Finishing
- Plastic Industry
- Beverage Fermentation
- Comfort Cooling
The chilled water system uses ambient air to remove heat from your food. The greatest advantage is that they help you save space and energy. The water chiller system uses water from an external cooling tower to cool your processed food. These chilled water cooling systems are long-lasting and have energy-efficient properties.
Water chillers are essential in cooling the air, and refrigerators ensure a comfortable indoor temperature. Furthermore, they’re employed in 3D printers to cool and prevent overheating.
Chilled Water System: FAQs
How do you maintain a chilled water system?
To maintain the water chiller system, inspect the fan control system, examine water flow, measure evaporator and condenser pressure, etc.
Why water chiller system use water?
Compared to other liquids, the heat of water is high, and at room temperature, it has the highest heat. Due to these properties, water is often used in cooling applications. Evaporation is the process required to turn a liquid into a gas.
What should be the minimum temperature for a chilled water system?
The chilled water system range is 5 to 11 ℃ or 6 to 12 ℃. With a six-degree temperature difference.
Conclusion
A water chiller is a cooling system that relies on water as a secondary refrigerant. They’re used for complex heating and large HVAC applications. A refrigerant loop is a main circuit or loop of a water chiller. This loop provides cooling, whereas the cold water is supplied to the consumer unit through the distribution system. To ensure quality, the VEVOR water chiller uses a standard R407 refrigerant that keeps systems up to 45KW cool during usage. It makes operation efficient and convenient and allows you to adjust the temperature ranges from 5 ℃ to 25 ℃. Not only this but even upon buying this industrial water chiller system, you’ll get this product at your doorstep without spending extra bucks.