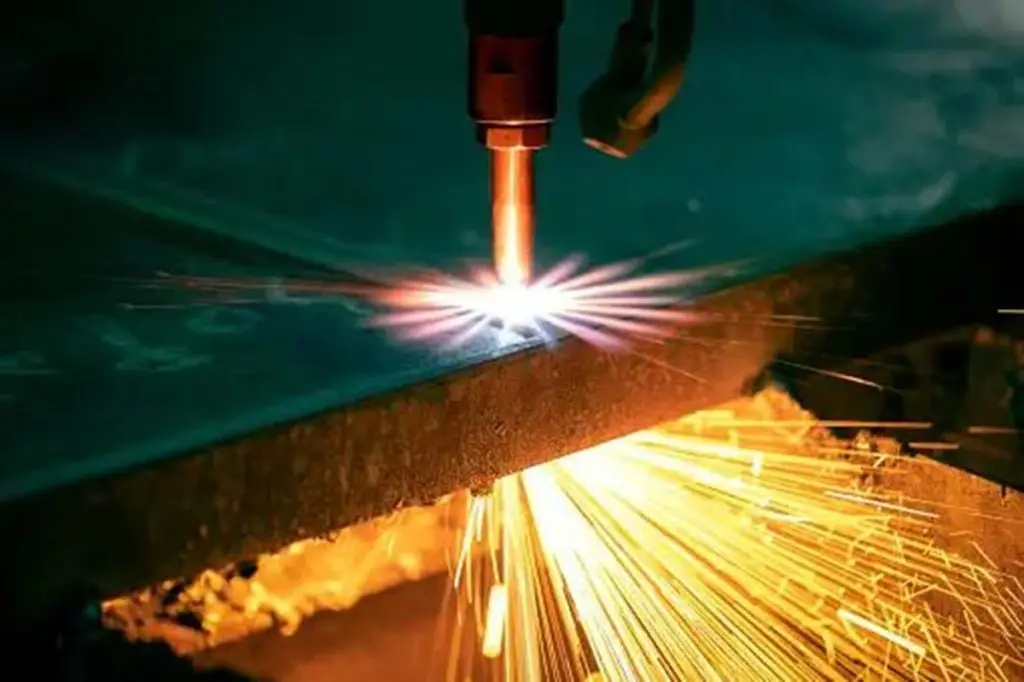
Does a plasma cutter need gas? Plasma cutting, a process that reaches temperatures over 20,000°C, utilizes ionized plasma cutter gas to precisely cut materials. Choosing the right gas for plasma cutter is crucial for optimizing both efficiency and cut quality.
In this guide, we’ll explore the various gas options available, their characteristics, and how they align with different materials and cutting requirements. Understanding the right type of gas for your plasma cutter is essential for anyone involved in metal cutting, ensuring precision and optimal results in every project.
Table of contents
What Gas Does a Plasma Cutter Use?
Understanding what gas does a plasma cutter use is essential for anyone involved in plasma cutting. The type of plasma cutter gas used can significantly influence the quality, efficiency, and cost of your cutting operations.

Compressed Air
Compressed air, essentially ordinary air under higher pressure, serves as a highly versatile and commonly used gas for plasma cutter operations. This air, mainly a mix of nitrogen and oxygen, becomes a practical cutting gas when compressed. Plasma cutters like the VEVOR Pilot Arc Plasma Cutter, especially the CUT50P model, effectively use compressed air, demonstrating its efficiency and practicality. The use of compressed air in plasma cutting offers significant benefits. It’s economical, as operators can produce it on-site using an air compressor, eliminating complex gas supply logistics. Its availability makes it a preferred choice for many.
Nitrogen
Nitrogen stands out in the plasma cutter gas field, especially for cutting aluminum and stainless steel. Known for its excellent cut quality, it produces smooth, precise cuts, crucial for high-quality finishes. This makes it a preferred choice for what gas does a plasma cutter use in these applications. It also extends the life of consumables like electrodes and nozzles, reducing both replacement costs and maintenance time.
When combined with air or CO2, nitrogen’s effectiveness increases. It achieves a balance between cut quality and speed with air, and when used with CO2, it enhances surface finish and speed. However, CO2 usage leads to higher costs and demands a more intricate gas supply system. This versatility cements nitrogen’s role as a valuable plasma cutting gas choice.
Argon
Argon gas is critical in plasma cutting, particularly for nonferrous metals such as aluminium and stainless steel. Its application in plasma cutters improves accuracy, resulting in cleaner cuts with less slag and heat distortion. Argon stabilizes the plasma arc, concentrating energy for cleaner, more controllable cuts, which is critical in high precision applications.
Furthermore, argon’s inert nature preserves the integrity of cut materials, preventing reactions that could alter their properties. When mixed with gases like hydrogen, it boosts cutting speed and efficiency. This versatility makes argon a significant player in metal fabrication, underlining its importance in industrial manufacturing for maintaining accuracy and quality.

Hydrogen
Hydrogen, a key gas for plasma cutter choice, excels in cutting thick materials like stainless steel and aluminum. Its primary attribute is the production of a hot flame, which is crucial for achieving deep, clean cuts. This makes hydrogen the preferred option for demanding cutting tasks.
The intense heat generated by hydrogen facilitates a cutting process that penetrates deeply and smoothly, making it ideal for thick and tough materials. Its ability to deliver such intense heat ensures that cuts are not only deep but also precise, addressing the need for high-quality finishes in demanding applications.
Oxygen
When considering gas for plasma cutter options, oxygen’s ability to react with mild steel to produce a finer, more controlled spray of molten metal is a key advantage. This reaction enhances the ejection of molten material from the cut, contributing to its clean and precise nature.
However, it’s important to balance these benefits with the higher operational costs associated with oxygen. This includes both the gas cost itself and the more frequent replacement of consumables due to its intense cutting action. Despite these factors, for tasks requiring top-notch quality and speed, especially in mild steel applications, oxygen holds its ground as a vital plasma cutting gas choice.
Argon-Hydrogen Mixtures
Argon-hydrogen mixtures are gaining recognition as a powerful choice for plasma cutting applications. This gas blend combines the stability of argon with the high heat conductivity of hydrogen, resulting in a versatile option for a wide range of cutting tasks. When used in plasma cutters, argon-hydrogen mixtures offer enhanced precision and efficiency. The argon stabilizes the plasma arc, ensuring controlled and focused cuts, while the hydrogen produces a hotter flame. This increased heat intensity is particularly advantageous when cutting thick materials like stainless steel and aluminum, as it enables deeper and cleaner cuts.
Additionally, argon-hydrogen mixtures can reduce the risk of material distortion and produce smoother edges, making them a preferred choice for demanding cutting tasks. This combination of stability, heat intensity, and precision makes argon-hydrogen mixtures a reliable solution for industries requiring high-quality plasma cutting results.

Nitrogen-Water Combination
The use of a nitrogen-water combination as the gas source in plasma cutting is a cost-effective and environmentally friendly option. Nitrogen is readily available and affordable, making it an attractive choice for industrial applications. When mixed with water, nitrogen becomes an efficient coolant for the plasma torch, helping to maintain its operational temperature and extend its lifespan.
This combination also generates a protective gas shield that prevents oxidation during the cutting process, resulting in clean, oxide-free cuts. Moreover, the nitrogen-water mixture minimizes the need for additional gas storage and transportation, reducing overall operational costs. This eco-conscious approach to plasma cutting aligns with sustainable manufacturing practices while delivering cost savings and quality results.

Plasma Gas Selection Guide
Here’s a comparative table, detailing the performance of different gas combinations for cutting mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum:
| Plasma Gas | Mild Steel | Stainless Steel | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compressed Air | High quality cuts, avoid risk of nitriding | Good cut quality and speed, Economical | Good cut quality and speed, Economical |
| Nitrogen & Air | High quality cuts, avoid risk of nitriding | High quality cuts, but some dross in thicker sections | Not recommended due to poor quality |
| Oxygen & Air | Excellent cut quality and speed | Not recommended for cause oxidation | Not recommended for cause oxidation |
| Argon-Hydrogen Mixtures | Not recommended | Excellent on thicknesses above 1/2″ | Excellent on thicknesses above 1/2″ |
| Nitrogen-Water Combination | Fair cut quality, Some dross, Excellent parts life | Excellent cut quality, Excellent parts life | Excellent cut quality, Excellent parts life |
When selecting plasma gases for cutting applications, it’s important to consider not only the material being cut but also the specific requirements of the cutting process, and how the gas will interact with the plasma cutting system. Here are some additional practical considerations for a plasma gas selection:
Process Efficiency: Efficiency in cutting can be influenced by gas selection. Gases that offer higher speeds can result in increased throughput but may also impact the wear on consumables and equipment differently.
Equipment Compatibility: Ensure that your plasma cutting system is equipped to handle the chosen gas or gas mixture without causing damage or undue wear on the system components.
Cost of Operation: Some gases may be less expensive upfront but could result in higher overall operating costs due to faster consumption rates or the need for more frequent replacement of cutting consumables.
Gas Mixtures: Experimenting with different gas mixtures can result in a range of qualities and efficiencies. Tailored gas mixtures can be developed for specific applications that require unique cutting characteristics.
Environmental Considerations: Some gases or gas mixtures may have environmental implications that need to be considered, such as the global warming potential or ozone depletion potential.
Cutting Environment: The working environment can also influence gas selection. For example, indoor cutting may have different ventilation requirements compared to outdoor cutting.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the chosen gases and their use comply with local, state, and federal regulations regarding safety, transportation, and storage.
FAQ
In this section, we’ll address some frequently asked questions about plasma cutting, providing clear and concise answers to enhance your understanding of this technology.
Do Plasma Cutters Run on Air?
Yes, many plasma cutters run on air. Compressed air is commonly used in plasma cutting for its availability and cost-effectiveness. This makes it a popular choice, especially for smaller-scale or portable plasma cutters.
Does Plasma Cutting Produce Fumes?
Plasma cutting generates smoke and fumes as it involves melting metal at high temperatures. These fumes can be hazardous if inhaled, thus necessitating proper ventilation and the use of protective equipment in the cutting area.
How Much Air Pressure Does It Take to Run a Plasma Cutter?
The air pressure required to operate a plasma cutter typically ranges from about 60 to 120 PSI (pounds per square inch). However, the exact requirement can vary depending on the specific model and the thickness of the material being cut.
Conclusion
In conclusion, selecting the right plasma cutter gas is a fundamental aspect of optimizing the performance and results of your plasma cutting tasks. This guide has provided a thorough overview of the kind of gas does a plasma cutter use, from compressed air to specialized gas mixtures. Understanding these gas types and their specific applications in plasma cutting is crucial for achieving the desired cutting quality and efficiency. Furthermore, it’s important to complement your knowledge of gases with the right plasma cutting accessories to enhance safety and effectiveness. Always refer to professional guidelines and manufacturer instructions to ensure the best outcomes in your plasma cutting projects.