Unveiling the Smelting Furnace: Transforming Raw Materials into Refined Ingots
Introduction: Harnessing the Power of the Smelting Furnace
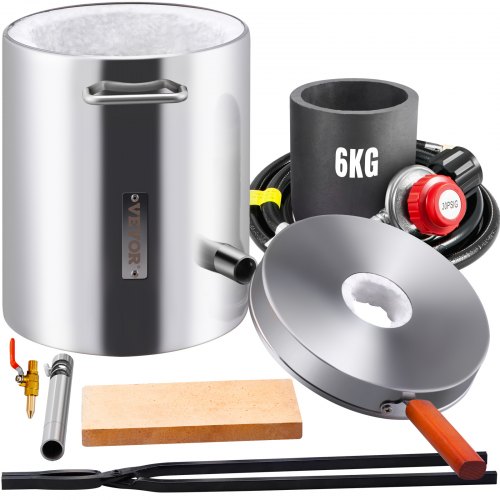
A smelting furnace stands as a symbol of industrial prowess, transforming raw materials into refined metal ingots through the application of intense heat. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the functionalities, benefits, and applications of smelting furnaces, empowering users to unlock the potential of metalworking and metallurgy.
Understanding Smelting Furnaces
Fundamental Principle: Extracting Metal from Ore
At its core, a smelting furnace utilizes heat to extract metal from ore or raw materials through a process known as smelting. By subjecting the raw materials to high temperatures, the furnace melts the metal-containing components, separating them from impurities and allowing them to be collected as molten metal.
Versatility: From Iron to Precious Metals
Smelting furnaces are versatile tools capable of processing a wide range of metals, from common ferrous metals like iron and steel to precious metals like gold and silver. Depending on the type of furnace and the materials being processed, smelting can occur in various forms, including blast furnaces, electric arc furnaces, and induction furnaces.
Types of Smelting Furnaces
Blast Furnaces: Traditional and Efficient
Blast furnaces are iconic structures in the metallurgical industry, known for their efficiency in producing large quantities of molten metal. These furnaces use a combination of coke, limestone, and iron ore as raw materials, with hot air blown into the furnace to facilitate combustion and smelting.
Electric Arc Furnaces: Modern and Flexible
Electric arc furnaces (EAFs) utilize electric arcs generated by graphite electrodes to melt scrap metal and other raw materials. These furnaces offer flexibility in terms of input materials and can accommodate a wide range of metal compositions, making them popular in steelmaking and recycling operations.
Induction Furnaces: Precise and Energy-Efficient
Induction furnaces employ electromagnetic induction to generate heat within the metal itself, resulting in precise temperature control and energy efficiency. These furnaces are commonly used for melting and refining metals with high melting points, such as copper, aluminum, and alloys.
Advantages of Smelting Furnaces
High Efficiency: Maximizing Metal Recovery
Smelting furnaces offer high efficiency in metal extraction and refining, minimizing waste and maximizing metal recovery from raw materials. By optimizing process parameters and furnace design, users can achieve high yields and purity levels, reducing production costs and environmental impact.
Flexibility and Customization: Tailored to Specific Needs
With their versatility and adaptability, smelting furnaces allow users to customize processing parameters and workflows to meet specific production requirements. Whether it's adjusting temperature profiles, controlling gas atmospheres, or refining metal alloys, users have the flexibility to optimize furnace operations for maximum efficiency and quality.
Considerations When Choosing a Smelting Furnace
Capacity and Throughput: Matching Production Demands
Select a smelting furnace with the appropriate capacity and throughput to match your production demands. Consider factors such as furnace size, melting rate, and batch processing capabilities to ensure optimal efficiency and productivity in your operations.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability: Minimizing Environmental Impact
Choose a smelting furnace with energy-efficient features and sustainable practices to minimize environmental impact and reduce operating costs. Look for technologies such as waste heat recovery, off-gas treatment systems, and alternative energy sources to enhance furnace efficiency and sustainability.
Conclusion: Empowering Metalworking Excellence with Smelting Furnaces
As we've explored, smelting furnaces play a vital role in the metalworking and metallurgical industries, enabling the transformation of raw materials into refined metal ingots with precision and efficiency. Whether it's blast furnaces, electric arc furnaces, or induction furnaces, these versatile tools offer endless possibilities for metal production, recycling, and innovation.
Take Action: Choose Your Perfect Smelting Furnace Today
Ready to harness the power of smelting furnaces for your metalworking needs? Explore a wide range of high-quality furnaces and metallurgical equipment, designed to meet the demands of professionals and enthusiasts alike. With the right furnace in your arsenal, you'll unlock new opportunities for creativity, efficiency, and excellence in metalworking and metallurgy.
FAQs about "Smelting Furnace"
What is a smelting furnace?
A smelting furnace is a type of furnace used to extract metal from ore by heating it to high temperatures in the presence of a reducing agent such as charcoal, coke, or flux. Smelting furnaces are commonly used in metallurgy and metalworking processes to produce raw metal ingots or alloys from mined ore or recycled scrap metal. These furnaces come in various designs and configurations depending on the specific requirements of the smelting process and the type of metal being extracted.
How does a smelting furnace work?
Smelting furnaces operate by subjecting metal ore or scrap metal to high temperatures in a controlled environment, causing the metal to melt and separate from impurities such as rock, slag, or other non-metallic components. The furnace is heated using a heat source such as natural gas, propane, electricity, or coke, which generates intense heat within the furnace chamber. As the temperature rises, the metal ore undergoes chemical reactions that result in the reduction of metal oxides to elemental metal, which then collects at the bottom of the furnace as molten metal. Impurities and slag rise to the surface and can be skimmed off or removed from the furnace.
What are the different types of smelting furnaces?
There are several types of smelting furnaces used in metallurgical processes, each tailored to specific applications and metal extraction methods. Blast furnaces are large, cylindrical furnaces used for high-volume production of iron and steel from iron ore, coke, and limestone. Cupola furnaces are smaller, vertical furnaces used for melting cast iron and other ferrous alloys in foundry operations. Reverberatory furnaces feature a shallow hearth and a low roof, ideal for smelting non-ferrous metals such as copper, lead, and zinc. Electric arc furnaces use electricity to generate heat for melting scrap