Exploring Water Chillers: Cooling Solutions for Various Applications
Introduction
Water chillers are essential components of cooling systems used in various industrial, commercial, and residential applications. In this guide, we'll delve into the fundamentals of water chillers, their types, applications, and benefits.
Understanding Water Chillers
What are Water Chillers?
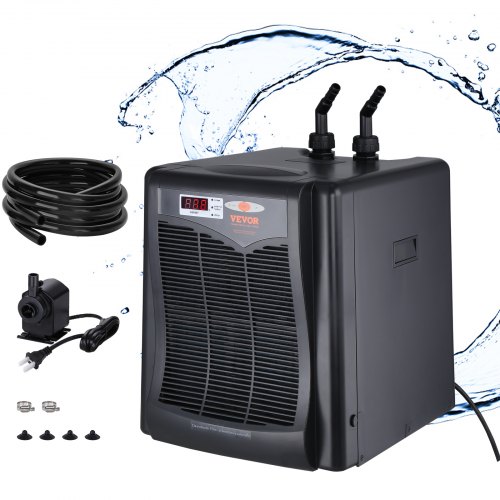
Water chillers are refrigeration systems designed to remove heat from water or other fluids to lower their temperature. They work by circulating chilled water through a heat exchanger, absorbing heat from the process or environment and dissipating it elsewhere, typically through air or water-cooled condensers.
Types of Water Chillers
-
Air-Cooled Chillers: These chillers use ambient air to dissipate heat from the refrigerant, making them suitable for applications where water availability or quality is limited. They are typically used in smaller-scale applications and environments with moderate ambient temperatures.
-
Water-Cooled Chillers: Water-cooled chillers utilize water as a cooling medium to remove heat from the refrigerant. They offer higher efficiency and cooling capacity compared to air-cooled chillers but require access to a reliable source of cooling water, such as a cooling tower or condenser water loop.
-
Evaporative-Cooled Chillers: Evaporative-cooled chillers combine the principles of air and water-cooled chillers by using both ambient air and water evaporation to dissipate heat. They offer improved efficiency and energy savings compared to traditional air-cooled chillers, especially in hot and dry climates.
Applications of Water Chillers
Industrial Processes
Water chillers play a crucial role in industrial processes that require precise temperature control, such as plastic molding, pharmaceutical manufacturing, food processing, and semiconductor fabrication. They ensure consistent product quality, optimize production efficiency, and prolong equipment lifespan by maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
HVAC Systems
In commercial buildings, water chillers are integral components of HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems used to provide comfort cooling and climate control. They cool water to supply chilled water to air handling units (AHUs), fan coil units (FCUs), and other cooling equipment to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures.
Medical and Laboratory Equipment
Water chillers are used in medical and laboratory settings to cool sensitive equipment and instruments, such as MRI machines, laser systems, chromatography systems, and electron microscopes. Precise temperature control is critical to ensure accurate test results, protect equipment from overheating, and maintain sample integrity.
Benefits of Water Chillers
Energy Efficiency
Water chillers offer high energy efficiency compared to traditional cooling methods, such as air conditioning or direct cooling with water. They use refrigeration cycles and heat exchange principles to remove heat from water or other fluids, minimizing energy consumption and operating costs.
Precise Temperature Control
Water chillers provide precise temperature control over a wide range of cooling capacities, allowing users to maintain stable process temperatures with minimal fluctuations. This precision is essential for applications requiring tight temperature tolerances and consistent product quality.
Environmental Sustainability
Water chillers can contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing water consumption and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions. Energy-efficient designs, use of eco-friendly refrigerants, and optimization of cooling processes help minimize the environmental impact of cooling systems.
Conclusion
Water chillers are versatile cooling solutions used in a wide range of industrial, commercial, and residential applications. By understanding the fundamentals of water chillers, their types, applications, and benefits, users can select the right chiller system to meet their specific cooling needs while maximizing energy efficiency, productivity, and environmental sustainability.
FAQs about Water Chillers
What is a water chiller?
A water chiller is a refrigeration device designed to cool water to a desired temperature for various industrial, commercial, or residential applications. It works by circulating water through a refrigeration system, where heat is removed from the water, resulting in a decrease in temperature. Water chillers are commonly used in HVAC systems, manufacturing processes, medical equipment, and food and beverage production to maintain optimal temperatures and ensure efficient operation.
How does a water chiller work?
A water chiller operates on the principle of vapor compression refrigeration, similar to a standard air conditioning system. It consists of several key components, including a compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator. The refrigeration cycle begins with the compressor compressing refrigerant gas, increasing its temperature and pressure. The hot, high-pressure refrigerant gas then flows to the condenser, where it releases heat to the surrounding air or water, causing it to condense into a liquid. The liquid refrigerant then passes through the expansion valve, where its pressure and temperature are reduced, allowing it to evaporate and absorb heat from the water in the evaporator. This process cools the water, which is then circulated to the desired location or application.
What are the types of water chillers available?
There are several types of water chillers available, each designed for specific applications and cooling requirements. Common types include:
-
Air-cooled chillers: These chillers use ambient air to dissipate heat from the refrigerant, eliminating the need for a separate cooling water source. They are compact, easy to install, and suitable for smaller-scale applications where water availability or quality is limited.
-
Water-cooled chillers: These chillers use water as a cooling medium to remove heat from the refrigerant. They typically require a separate cooling tower or water source for heat rejection and are commonly used in larger-scale applications where higher cooling capacities are required.
-
Portable chillers: These compact and mobile chillers are designed for temporary or on-the-go cooling needs, such as event cooling, emergency cooling, or process cooling in remote locations.
-
Absorption chillers: These chillers use heat energy, such as steam or hot water, to drive the refrigeration cycle, making them more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly compared to traditional vapor compression chillers. They are commonly used in industrial and commercial applications with access to waste heat or renewable energy sources.
What are the benefits of using a water chiller?
Using a water chiller offers several benefits, including:
-
Temperature control: Water chillers provide precise temperature control, allowing users to maintain consistent and optimal operating temperatures for equipment, processes, and products.
-
Energy efficiency: Water chillers are often more energy-efficient than other cooling methods, especially when used in conjunction with energy-saving features such as variable-speed compressors or heat recovery systems.
-
Versatility: Water chillers can be used in a wide range of applications and industries, from air conditioning and refrigeration to process cooling and medical equipment cooling.
-
Reliability: Water chillers are designed for continuous operation and are built with durable components to ensure reliable performance even under demanding conditions.
How do I choose the right water chiller for my needs?
When choosing a water chiller, consider factors such as:
- Cooling capacity and temperature range required for your specific application.
- Available space for installation and access to cooling water sources or ventilation.
- Energy efficiency and operating costs, including initial investment, maintenance, and lifecycle expenses.
- Compatibility with existing equipment and systems, including controls, piping, and power supply requirements.
- Noise levels and environmental considerations, such as local regulations or emissions standards.
- Manufacturer reputation, warranty coverage, and technical support availability to ensure reliable operation and support throughout the chiller's lifespan.